How to pass tool outputs to chat models
This guide assumes familiarity with the following concepts:
Some models are capable of tool calling - generating arguments that conform to a specific user-provided schema. This guide will demonstrate how to use those tool cals to actually call a function and properly pass the results back to the model.
First, let’s define our tools and our model:
import { z } from "zod";
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
const addTool = tool(
async ({ a, b }) => {
return a + b;
},
{
name: "add",
schema: z.object({
a: z.number(),
b: z.number(),
}),
description: "Adds a and b.",
}
);
const multiplyTool = tool(
async ({ a, b }) => {
return a * b;
},
{
name: "multiply",
schema: z.object({
a: z.number(),
b: z.number(),
}),
description: "Multiplies a and b.",
}
);
const tools = [addTool, multiplyTool];
Pick your chat model:
- OpenAI
- Anthropic
- FireworksAI
- MistralAI
- Groq
- VertexAI
Install dependencies
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm i @langchain/openai
yarn add @langchain/openai
pnpm add @langchain/openai
Add environment variables
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-api-key
Instantiate the model
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
const llm = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
temperature: 0
});
Install dependencies
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm i @langchain/anthropic
yarn add @langchain/anthropic
pnpm add @langchain/anthropic
Add environment variables
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your-api-key
Instantiate the model
import { ChatAnthropic } from "@langchain/anthropic";
const llm = new ChatAnthropic({
model: "claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
temperature: 0
});
Install dependencies
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm i @langchain/community
yarn add @langchain/community
pnpm add @langchain/community
Add environment variables
FIREWORKS_API_KEY=your-api-key
Instantiate the model
import { ChatFireworks } from "@langchain/community/chat_models/fireworks";
const llm = new ChatFireworks({
model: "accounts/fireworks/models/llama-v3p1-70b-instruct",
temperature: 0
});
Install dependencies
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm i @langchain/mistralai
yarn add @langchain/mistralai
pnpm add @langchain/mistralai
Add environment variables
MISTRAL_API_KEY=your-api-key
Instantiate the model
import { ChatMistralAI } from "@langchain/mistralai";
const llm = new ChatMistralAI({
model: "mistral-large-latest",
temperature: 0
});
Install dependencies
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm i @langchain/groq
yarn add @langchain/groq
pnpm add @langchain/groq
Add environment variables
GROQ_API_KEY=your-api-key
Instantiate the model
import { ChatGroq } from "@langchain/groq";
const llm = new ChatGroq({
model: "mixtral-8x7b-32768",
temperature: 0
});
Install dependencies
- npm
- yarn
- pnpm
npm i @langchain/google-vertexai
yarn add @langchain/google-vertexai
pnpm add @langchain/google-vertexai
Add environment variables
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=credentials.json
Instantiate the model
import { ChatVertexAI } from "@langchain/google-vertexai";
const llm = new ChatVertexAI({
model: "gemini-1.5-flash",
temperature: 0
});
Now, let’s get the model to call a tool. We’ll add it to a list of messages that we’ll treat as conversation history:
import { HumanMessage } from "@langchain/core/messages";
const llmWithTools = llm.bindTools(tools);
const messages = [new HumanMessage("What is 3 * 12? Also, what is 11 + 49?")];
const aiMessage = await llmWithTools.invoke(messages);
console.log(aiMessage);
messages.push(aiMessage);
AIMessage {
"id": "chatcmpl-9p1NbC7sfZP0FE0bNfFiVYbPuWivg",
"content": "",
"additional_kwargs": {
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_RbUuLMYf3vgcdSQ8bhy1D5Ty",
"type": "function",
"function": "[Object]"
},
{
"id": "call_Bzz1qgQjTlQIHMcEaDAdoH8X",
"type": "function",
"function": "[Object]"
}
]
},
"response_metadata": {
"tokenUsage": {
"completionTokens": 50,
"promptTokens": 87,
"totalTokens": 137
},
"finish_reason": "tool_calls",
"system_fingerprint": "fp_400f27fa1f"
},
"tool_calls": [
{
"name": "multiply",
"args": {
"a": 3,
"b": 12
},
"type": "tool_call",
"id": "call_RbUuLMYf3vgcdSQ8bhy1D5Ty"
},
{
"name": "add",
"args": {
"a": 11,
"b": 49
},
"type": "tool_call",
"id": "call_Bzz1qgQjTlQIHMcEaDAdoH8X"
}
],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 87,
"output_tokens": 50,
"total_tokens": 137
}
}
2
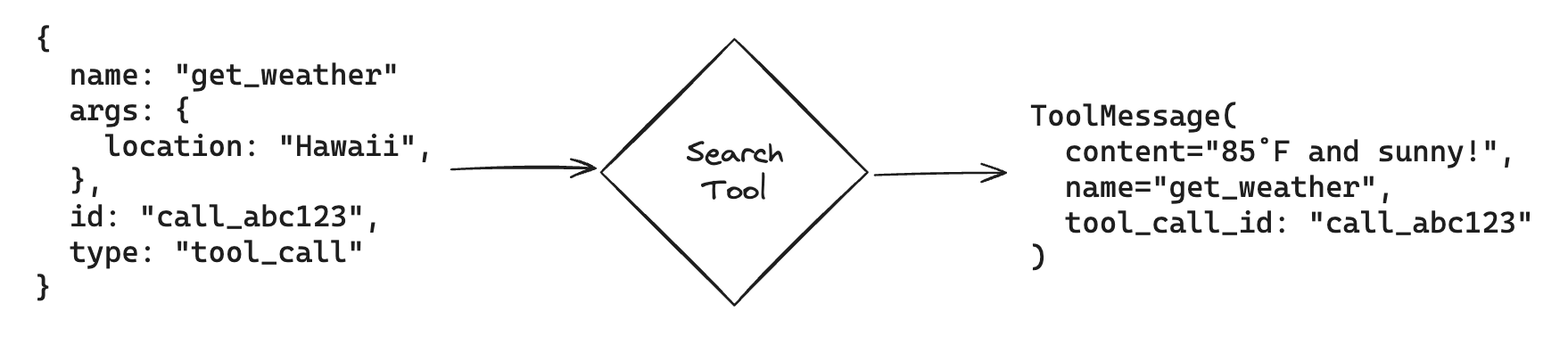
Next let’s invoke the tool functions using the args the model populated!
Conveniently, if we invoke a LangChain Tool with a ToolCall, we’ll
automatically get back a ToolMessage that can be fed back to the
model:
This functionality requires @langchain/core>=0.2.16. Please see here for a guide on upgrading.
If you are on earlier versions of @langchain/core, you will need to access construct a ToolMessage manually using fields from the tool call.
const toolsByName = {
add: addTool,
multiply: multiplyTool,
};
for (const toolCall of aiMessage.tool_calls) {
const selectedTool = toolsByName[toolCall.name];
const toolMessage = await selectedTool.invoke(toolCall);
messages.push(toolMessage);
}
console.log(messages);
[
HumanMessage {
"content": "What is 3 * 12? Also, what is 11 + 49?",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {}
},
AIMessage {
"id": "chatcmpl-9p1NbC7sfZP0FE0bNfFiVYbPuWivg",
"content": "",
"additional_kwargs": {
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_RbUuLMYf3vgcdSQ8bhy1D5Ty",
"type": "function",
"function": "[Object]"
},
{
"id": "call_Bzz1qgQjTlQIHMcEaDAdoH8X",
"type": "function",
"function": "[Object]"
}
]
},
"response_metadata": {
"tokenUsage": {
"completionTokens": 50,
"promptTokens": 87,
"totalTokens": 137
},
"finish_reason": "tool_calls",
"system_fingerprint": "fp_400f27fa1f"
},
"tool_calls": [
{
"name": "multiply",
"args": {
"a": 3,
"b": 12
},
"type": "tool_call",
"id": "call_RbUuLMYf3vgcdSQ8bhy1D5Ty"
},
{
"name": "add",
"args": {
"a": 11,
"b": 49
},
"type": "tool_call",
"id": "call_Bzz1qgQjTlQIHMcEaDAdoH8X"
}
],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 87,
"output_tokens": 50,
"total_tokens": 137
}
},
ToolMessage {
"content": "36",
"name": "multiply",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {},
"tool_call_id": "call_RbUuLMYf3vgcdSQ8bhy1D5Ty"
},
ToolMessage {
"content": "60",
"name": "add",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {},
"tool_call_id": "call_Bzz1qgQjTlQIHMcEaDAdoH8X"
}
]
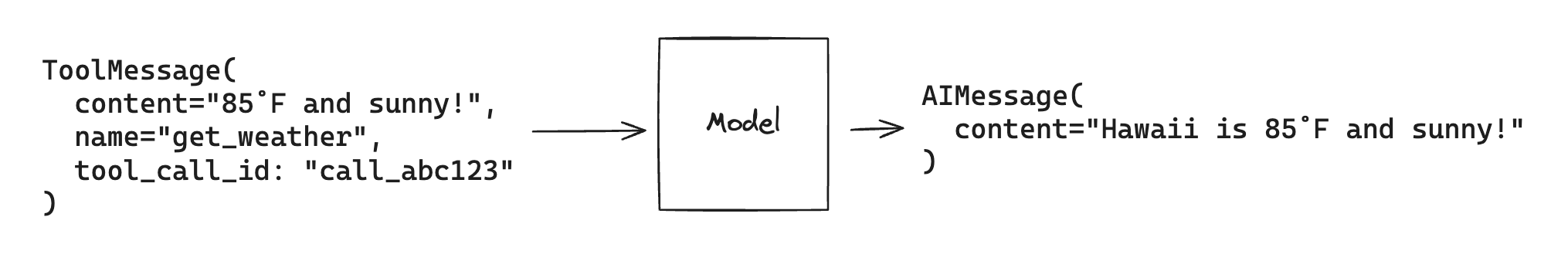
And finally, we’ll invoke the model with the tool results. The model will use this information to generate a final answer to our original query:
await llmWithTools.invoke(messages);
AIMessage {
"id": "chatcmpl-9p1NttGpWjx1cQoVIDlMhumYq12Pe",
"content": "3 * 12 is 36, and 11 + 49 is 60.",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {
"tokenUsage": {
"completionTokens": 19,
"promptTokens": 153,
"totalTokens": 172
},
"finish_reason": "stop",
"system_fingerprint": "fp_18cc0f1fa0"
},
"tool_calls": [],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 153,
"output_tokens": 19,
"total_tokens": 172
}
}
Note that each ToolMessage must include a tool_call_id that matches
an id in the original tool calls that the model generates. This helps
the model match tool responses with tool calls.
Tool calling agents, like those in LangGraph, use this basic flow to answer queries and solve tasks.
Related
You’ve now seen how to pass tool calls back to a model.
These guides may interest you next:
- LangGraph quickstart
- Few shot prompting with tools
- Stream tool calls
- Pass runtime values to tools
- Getting structured outputs from models